Making plans for a party or picking out office outfits according to our waxing schedules – all women do this. But what if you had to take appointments to the parlor for several times in a month – seems expensive and exhausting right? Women with excessive hair on their body will relate to the latter situation – they have hirsutism.
HIRSUTISM
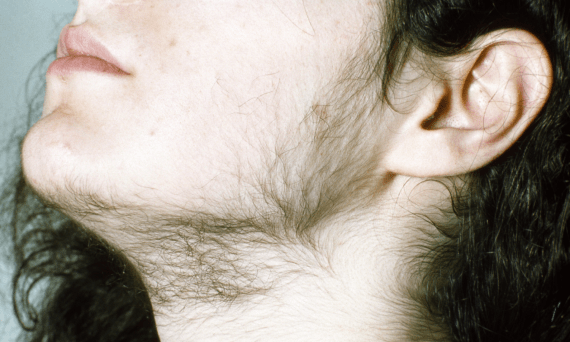
What Is The Difference Between Normal Hair And The Hair Developed Due To Hirsutism?
Every woman has facial and body hair that is usually fine and light in color. But the hair grown in an individual with hirsutism is coarse and dark. Women with hirsutism have male pattern hair growth along with masculine physical traits (virilization).
What Are The Chances Of Developing Hirsutism?
Several factors may increase the risk your risk for developing hirsutism, which include:
- Family history –History of conditions that run in the family like polycystic ovary syndrome and congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
- Lineage – Women having Middle Eastern, Mediterranean, and South Asian ancestry are more likely to have more body hair compared to others.
- Obesity – Increased weight may lead to increased androgen production leading to hirsutism.
How Will I Know If I Have Hirsutism?
Besides excessive hair growth, other common symptoms experienced by the women include:
- Acne
- Balding
- Deepening of the voice
- Increased muscle mass
- Decreased breast size
- Enlargement of clitoris
What Conditions Can Cause Hirsutism?
PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) is the common condition that causes hirsutism, accounting for around 80% of all the cases. Idiopathic familial hirsutism is the second common cause that accounts for about 15% of the cases. However, there are many other causes of hirsutism such as:
- Ovarian disorders – ovarian tumors or ovarian hyperthecosis
- Adrenal disorders – congenital or delayed onset adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal tumors or Cushing’s syndrome
- Thyroid disorders – hypothyroidism
- Pituitary Disorders – prolactinoma or acromegaly
- Certain Drugs – Anabolic steroids (danazol), Testosterone, Oral contraceptives with high progesterone content, Metoclopramide, Phenothiazines, Minoxidil, Phenytoin, Diazoxide.
- Other conditions – Hyperinsulinemia, HAIR-AN (Hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, acanthosis nigricans) syndrome, SAHA (Seborrhea, acne, hirsutism, acanthosis nigricans) syndrome
How Can One Diagnose Hirsutism?
The clinical evaluation of the condition includes the patient’s history and physical examination. Usually, women with mild hirsutism need no further investigations. Instead, women with moderate to severe hirsutism may need to undergo investigations to rule out hyperandrogenism. In cases where there is a sudden onset, rapid growth of hair and virilization signs, it is important to rule out ovarian and adrenal neoplasia.
The common laboratory investigations for hirsutism include measuring the testosterone prolactin, androstenedione levels in the blood along with luteinizing hormone (LH), Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), etc. Lipid profile, blood sugar and insulin resistance studies are also used to identify the cause of hirsutism.
Imaging tests such as ultrasonography, computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are recommended as required to rule out ovarian, adrenal neoplasia and pituitary adenomas.
What Is The Treatment Approach For Hirsutism?
Unwanted hairs on your body is not a direct condition, rather it is a manifestation of the underlying health problems. Some of these conditions can be cured permanently, while others need to be managed through prolonged treatment.
The most effective treatment line of hirsutism involves a combination of hair removal and medical therapy.
- The common medical therapy for managing hirsutism includes the use of oral contraceptives for at least six months. Others may include androgen suppressants, glucocorticoids, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, antiandrogens, etc.
- A wide range of hair removal options such as plucking, waxing, shaving and depilatory creams are also available.
- Topical creams (Eflornithine hydrochloride) are also available that can help to slow down the growth of new hair. Hence, they are used along with laser therapy for better response.
Are There Permanent Hair Removal Treatments Available For Hirsutism?
The treatment of hirsutism depends on the underlying cause. Once the cause for hirsutism is cured, your abnormal hair also tends to decrease gradually. However, in majority of cases, hirsutism requires an ongoing treatment.
There are treatments available that helps you to get rid of the unwanted hair for longer duration. Laser hair removal and electrolysis are such treatments that may provide permanent results when compared to waxing or shaving. However, none of the treatments may make your hair to go away completely, instead they reduce their growth and decrease the amount of the unwanted hair.
Does Obesity Lead To Hirsutism?
Hirsutism is found to be more common in women with higher Body Mass Index (BMI). Research says that the association of hirsutism with obesity could be related to the increased insulin resistance and androgen production by the adipose tissue
How Does Weight Loss Help In Managing The Condition?
Weight loss helps in decreasing insulin levels in the serum along with androgen levels in the body. It also decreases the conversion of androstenedione to testosterone. Studies suggest that even a 5% decrease in body weight helps to lower the androgen levels and the amount of unwanted hair.
What Is The Hair Cycle?
The life of a hair (from developing from a hair follicle to falling out) is divided into 4 cycles:
- Anagen phase: This is the growing phase and lasts for 2-7 years. This phase determines the length of the hair.
- Catagen phase: This is a transitional phase in which the hair follicle shrinks. This phase lasts for around 10 days
- Telogen phase: This is the phase in which the hairs are at a resting phase. This phase lasts for around 3 months. Around 10% of hairs are in this phase at any time.
- Exogen phase: In this phase, in which the old hair sheds out. Normally, 50-150 hairs fall in a day.
What Is The FG Score For Hirsutism?
FG score is a widely used score to evaluate hirsutism in women. This system evaluates various body areas for hair growth and scores from 0-4(absent to severe hirsutism). Total score of >8 is diagnostic of hirsutism.
How Is Metabolic Syndrome And Hirsutism Associated?
Both hirsutism and metabolic syndrome in women are complications of polycystic ovarian disease. Any woman with hirsutism associated with PCOD, should be evaluated for metabolic syndrome.
