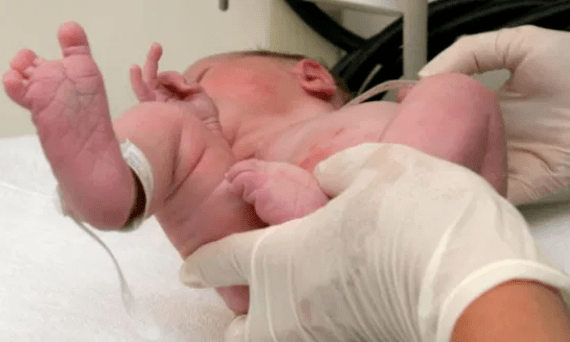
If your baby is treated for ambiguous genitalia, it will help your baby with his/her identity and also up lift their emotional wellbeing. It begins after a thorough diagnostic process like imaging test to view the presence of internal female sex organs in relation to external private parts, or a blood test to know the hormonal levels, or to confirm any underlying cause, if any.
The available treatment options of ambiguous genitalia may include medications such as a hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to correct the hormonal imbalance or a surgery to remove or create appropriate private parts and improve ability to reproduce or become pregnant. Parents can take part in decision making of the treatment and choose an appropriate treatment for their child. Sometimes, the treatment may be postponed until the child is mature enough to decide about the choice of gender.